Challenges and Opportunities for Software Developers on the Rise of Powerful AI
Thu 02/01/2025 15m read 1056 views
Choosing the Right Tool for Business Management: Web App vs Mobile App
Managing a business efficiently in today’s digital era often boils down to the right choice of tools. Among these, web apps and mobile apps are two powerful platforms for streamlining operations and boosting productivity. But which one is better suited for managing a business? Let’s explore their definitions, benefits, drawbacks, and how to strike a balance for optimal efficiency, including how data science complements these tools.
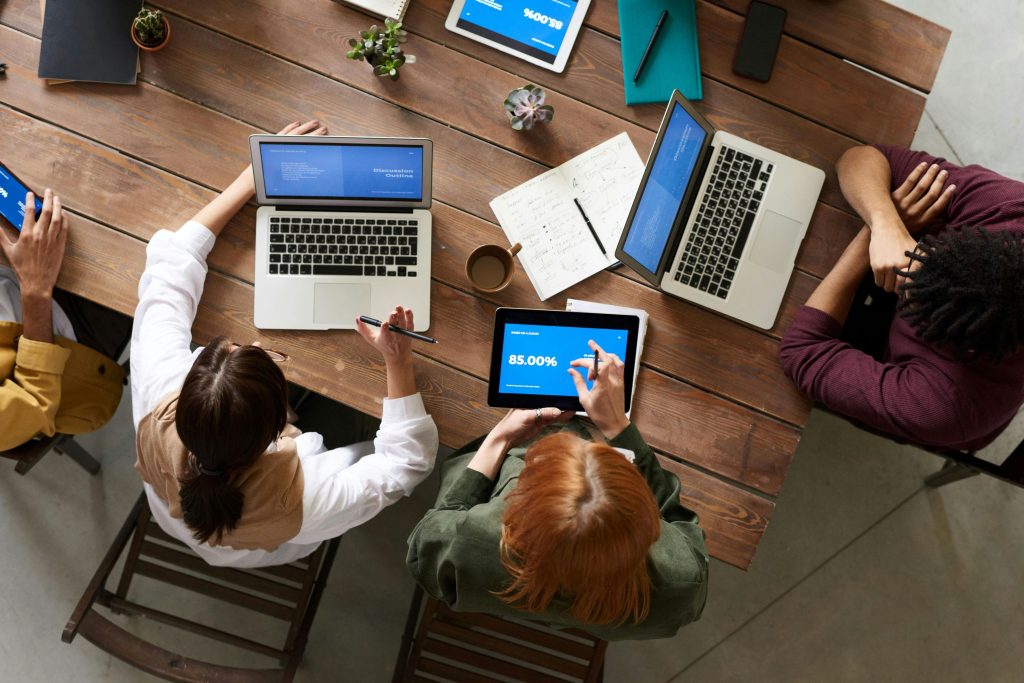

What Is a Web App?
A web app is a software application accessible through a web browser. It’s hosted on a remote server, eliminating the need for downloads or installations. Examples include Google Docs, Slack (web version), and Trello.
Pros of Web Apps:
- Accessibility: Accessible on any device with a browser and internet connection.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Easier to maintain and update since there’s no need to manage multiple operating systems.
- Scalability: Ideal for tasks requiring large displays or intricate dashboards.
- Compatibility: Operates seamlessly across various devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and phones.
- Data Science Integration: Web apps often host robust analytics tools, helping businesses harness data science for reporting and forecasting.
Cons of Web Apps:
- Internet Dependence: Requires a stable internet connection for access.
- Performance Limitations: May not leverage the full power of mobile hardware.
- Limited Offline Access: Functionality is restricted when offline.
What Is a Mobile App?
A mobile app is a software application specifically designed for mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. Mobile apps are downloaded and installed via app stores like Google Play or Apple’s App Store.
Pros of Mobile Apps:
- Offline Functionality: Many apps work without an internet connection.
- Enhanced User Experience: Designed for touch interfaces and optimized for smaller screens.
- Push Notifications: Enables real-time communication with users.
- Hardware Integration: Accesses device features like GPS, camera, and accelerometer for advanced functionality.
- Real-Time Insights: Data science integrated into mobile apps provides actionable insights directly to employees in the field.
Cons of Mobile Apps:
- Development Costs: Requires separate development for Android, iOS, and other platforms.
- Maintenance: Updates must be rolled out for each operating system.
- Storage Requirements: Occupies device memory.
Who Should Use Web Apps and Mobile Apps?
To maximize productivity, it’s crucial to assign the right tool to the right role.
Web Apps for Specific Roles:
- Managers and Administrators: Ideal for roles that involve heavy data analysis, reporting, and managing dashboards. Data science tools integrated into web apps empower strategic decision-making.
- Accountants: The larger screen and access to spreadsheets and accounting tools make web apps indispensable.
- Content Creators and Designers: Suitable for tasks requiring detailed interfaces and advanced software tools.
Mobile Apps for Specific Roles:
- Field Employees: Sales representatives, delivery personnel, or technicians benefit from real-time updates, offline access, and data-driven task optimization.
- Customer Support: Quick access to customer information and chat tools on the go.
- Team Leaders: Managing tasks and coordinating with teams in real time while mobile.
How Data Science Enhances Business Management
Data science plays a crucial role in amplifying the effectiveness of both web and mobile apps in business management:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Predictive analytics tools integrated into web apps allow businesses to forecast trends and optimize strategies.
- Personalized Experiences: Mobile apps use customer behavior data to provide tailored recommendations and services.
- Operational Efficiency: Data-driven insights streamline workflows, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing resource allocation.
- Employee Productivity: Analytics within apps enable real-time performance monitoring, ensuring optimal task distribution.
- Market Trends Analysis: Both platforms use advanced analytics to help businesses stay ahead of market shifts.
By embedding data science directly into web and mobile applications, businesses can create systems that are not only reactive but also predictive, driving proactive management strategies.
What Is a Perfect System for Business Management?
The perfect system is not about choosing one over the other but integrating both web apps and mobile apps to ensure flexibility and adaptability. Here’s how:
- Seamless Integration: Ensure data synchronization between web and mobile platforms for consistency.
- Role-Based Access: Assign platform access based on job roles and requirements.
- Scalability: Use a robust backend infrastructure to support simultaneous usage.
- Offline and Online Modes: Design hybrid apps where mobile apps function offline and sync with the web app when online.
- Data-Driven Insights: Incorporate data science tools for analytics, ensuring data-backed decision-making across all levels.
- User Training: Equip employees with adequate training to maximize the benefits of both platforms.
Conclusion
When managing a business, the debate between web apps and mobile apps is not about competition but complementarity. Web apps excel in offering a comprehensive view and handling complex tasks, while mobile apps thrive in mobility and real-time responsiveness. By integrating data science into both platforms, businesses can unlock smarter systems capable of adapting to changing needs. The synergy of web apps, mobile apps, and data science provides businesses with unparalleled flexibility, productivity, and efficiency. This integrated approach ensures that every role in the organization is equipped with the best tools for success.
Related articles